Managing Growth in New Venture
- After launching a new business, the focus is shifted to consolidating technology, after that for consolidating marketing efforts and once full capacity utilization has become possible because of booking of orders, attention has to be drawn towards growth. Growth is the best strategy for survival. Therefore, in this article, we will focus on understanding issues related to growth; meaning of growth, need for growth and factors affecting growth before discussing characteristics of high growth firms. Strategies for growth are discussed after that, where emphasis is on direction of growth and sub-strategies associated with each possible direction
- Characteristics of High Growth: The growth of a firm had mainly remained a topic for economists to discuss for a long time before Young (1961) wrote, “The phenomenon of corporate growth – the product of wide range of contributing variables – has fascinated and baffled economists, executives and investors for as long as competitive business organizations have existed”.
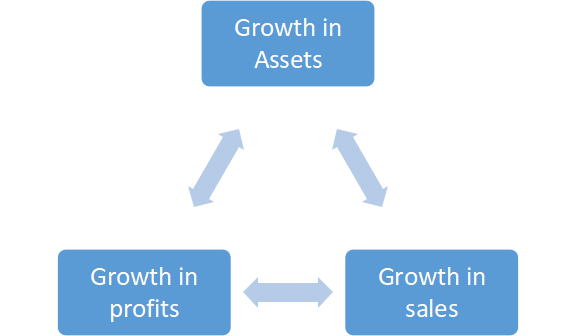
- What is Growth? In the world of real business, the term ‘growth’ is often used, because a competitive environment has compelled business firms to view growth as the best survival strategy that may decide whether a firm will prevail or perish. Growth of a company is occasionally understood with reference to change in quantity sales, naira sales, gross or net investment in asset, profit or profitability. The term ‘growth’ is also used to indicate change in market share or earning per share or market price of share. Stanford Research Institute, an applied research centre in Menlo Park, California, (Young, 1961) had conducted a fundamental study and developed a formula for growth ranking of firms. They had included three growth measures: the percentage increasein sales (growth in size), in net profits, and in the price of the company’s common stock.
- In this article, the growth of a firm has been defined in terms of change in gross block. Gross block means the purchase value of fixed assets; and change in gross block means new investment in the firm’s fixed assets. It was observed there that a strong positive correlation existed between the movement in market price of share and change in the gross block of the firms. Asset growth provides much needed conditions for growth in sales and profit. It must be followed by growth in sales through technological consolidation first and then through market consolidation. Sales growth should lead to profit growth, if the consolidation phase is suitably managed. In turn, the retained profit would create the necessary pre-requisite conditions for the growth in asset. The cycle of firm’s growth would, thus, continue.
- Why Should a Firm Grow? Some firms grow through product-diversification to minimize business risk, and some expand their operations globally to achieve market-line diversification needed for spreading out the risk. Reasons for growth vary from time to time, depending upon the situation. But ultimately value maximization should be the firm’s objective.
- Factors Inducing Growth: The entrepreneur’s attitude towards growth has a tremendous impact on the quality of growth. Quality means sustainability. Sustainability brings out the full potential of the firm for maximizing firm’s value. Demand-push growth is an unplanned growth and is not a sustainable growth. It essentially means just a routine or mechanical response to the opportunity coming on the way of a business firm. The entrepreneur responds to the growth in demand of their product, and invest fresh amount of funds usually in expansion activities. Any change in pattern of demand would change a firm’s financial position in a demand-push growth. Proactive growth requires strategic planning. Constant scanning of the environment for opportunities and threats, continuous study of internal strength and weaknesses, and strategies for establishing a viable fit between resources and opportunities are the characteristics of a proactive firm.
- Characteristics of an entrepreneur
- Characteristics of business
- Business practices of the enterprise
- Human resources
- (i) Characteristics of an entrepreneur: An entrepreneur who possesses the following qualities is likely to steer his/her business towards a high growth trajectory:
* Passion
* Vision to attain dream
* Persistence to work relentlessly and tirelessly
* High Self-efficacy to attain one’s objective
* Resource Skills
* Intelligence - (ii) Characteristics of business : Some characteristics of a firm would be conducive to high growth. Some important ones are as follows:
* Strong commitment for growth
* Collaborative Growth Strategies
* Good Planning Strength
* Vibrant Organization Stages of evolution and revolution of an organization.
Usually in the infancy stage, vibrancy is derived from the visionary leader.When employees acquire confidence and understanding of business the further growth of business is ensured by granting little autonomy and guiding behavior of the leader. But when the crisis of autonomy arises, delegation would become the key for ensuring fast growth. When powers are delegated controls are lost over a time. When that happens, leaders test lies in coordinating skills; if the leaders effectively coordinate efforts of all departments and managers, the growth remains on a good trajectory. However, coordination would require rules and processes, the excess of which would result into red-tap organization. Collaborative spirit may fade away and result into inter-personal crisis. Business is disintegrated at this stage and divisions are spun-off to make them into separate firms, who start from the scratch. Reshaping of an organization structure as per the first sign of any type of crisis, supported with a suitable leadership, is very much essential. Otherwise an organization may start losing its effectiveness.- (iii) Business practices of the enterprise: Business practices are important for a long-term play of business, which grows fast. It is matter of rules, procedures, documentation and overall culture that can deliver customer satisfaction and build credibility. This can be achieved through quality product and services, offering of value for money to customers and innovations that may fullfil customer needs.
- (iv) Human Resources: Human resources are of utmost importance for the survival and growth of a business. It is also true that a growing firm can easily offer opportunities for employees to grow. Growth here does not mean financial advancement, but mostly professional advancement. Be selective in hiring employees, especially on key positions. Search for the right people and offer opportunities in monetary terms and growth terms.
Strategies for Growth
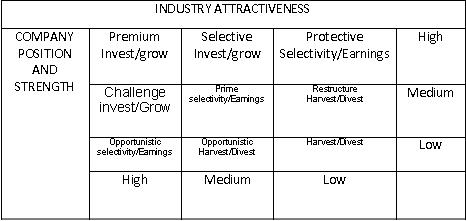
The issue of growth is strategic in nature, therefore, it involve strategic thinking, and hence, application of SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis model must suit the need for answering a particular question, which is related to either direction of growth or rate of growth or strategy for growth. Strategic models are described and their applications are explained in each of these fields of strategic decisions in the following sections of this article.- To continue reading: Click here
- Characteristics of a High Growth Firm: Proactive growth is possible with entrepreneurial zeal of managers and owners of a business. The high growth opportunity arises out of four factors (quadrants) combining with each other, namely;
Summary
Let us recapitulate the important concepts discussed in this unit:
Starting a venture is easy but nurturing it for growth is more challenging because there is only one way of survival, and that is through growth.
Growth comes in phases, first investment in business grows, and then it shall result in growth in sales, and then profit and again growth in investment. The cycle begins with investment growth made in a very strategic way.
However, if a venture does not grow in the right direction chances of earning profits or improving market share may reduce. The choice of growth direction can be made by the application of product-market matrix in which strengths and weaknesses around product and markets of the existing business are assessed and trajectory is decided where the growth lies.
The application of product-market matrix gives many options for the growth direction. Based on the one chosen with the application of this model, further applications of product life cycle, BCG, GE models would give further clarity about the area where focus must be laid for growth.
The next question is about the rate of growth. Slower or faster growth rate would bring sub-optimal results and sometimes even negative results.
Another important decision area is how to grow, that is growth strategies.
Growth strategies are broadly divided into two parts, internal growth and external growth. Internal growth is more organic and that comes with greenfield projects wherein a firm starts a new project afresh and takes a risk of gestation period and associated risks. In external growth strategies mergers and acquisitions or other types of collaborative growth are included.
A well-chosen growth path, growth rate and growth strategy will work only if proper human resource management as well as appropriate organizational systems are in place.